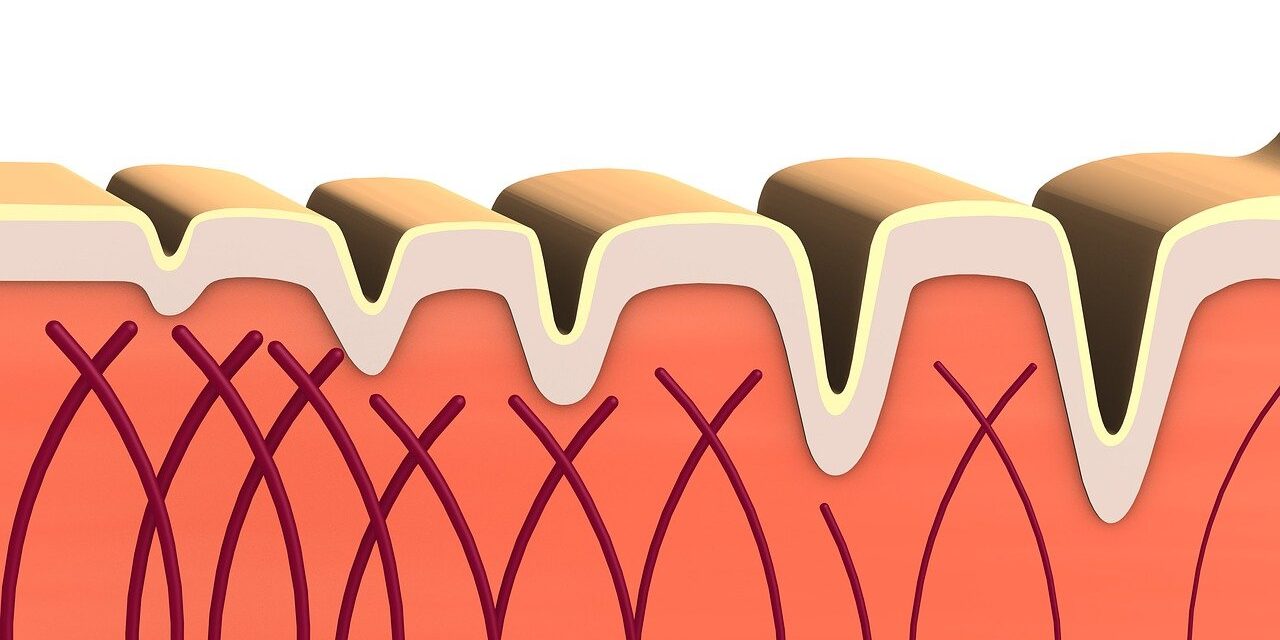
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and serves as a foundational component of skin, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments, and connective tissue, with structural biology research published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information explaining how collagen fibers provide tensile strength, elasticity, and tissue resilience throughout the body.
Why Collagen Is Important for Overall Health
Collagen plays a critical role in maintaining tissue integrity by supporting cellular scaffolding, wound healing, and structural repair processes, as demonstrated in peer-reviewed biomedical research that examines collagen’s function in connective tissue regeneration and age-related tissue decline.
Types of Collagen Found in the Human Body
Although more than 28 types of collagen have been identified, five account for the majority found in humans, with molecular classification studies published by the National Library of Medicine detailing how each type serves a distinct structural and biological role.
Type I Collagen
Type I collagen is the most abundant form and is primarily found in skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments, with its fibrillar structure and biomechanical properties outlined in biochemical research literature that explores collagen’s role in tissue strength and durability.
Type II Collagen
Type II collagen is concentrated in cartilage and supports joint cushioning and shock absorption, with evidence from human clinical trials demonstrating its importance in maintaining cartilage structure and joint mobility.
Type III Collagen
Type III collagen supports skin elasticity and vascular integrity and often appears alongside Type I collagen, as described in vascular biology research examining connective tissue development and blood vessel support.
Type IV Collagen
Type IV collagen is a major structural component of basement membranes that support filtration and tissue separation, with functional analysis provided by cellular biology studies investigating membrane stability and organ architecture.
Type V Collagen
Type V collagen plays a regulatory role in collagen fiber assembly and tissue formation, with developmental research published by academic connective tissue journals highlighting its contribution to collagen organization.
Collagen and Gut Health
Collagen contains glycine, an amino acid that supports gut lining integrity, with gastrointestinal research hosted by the National Library of Medicine examining amino acid support for intestinal barrier function and digestive health.
Natural Food Sources of Collagen
Collagen is found primarily in animal-based foods such as bone broth, chicken skin, fish skin, and connective tissue from beef and pork, while vitamin C is required for collagen synthesis according to guidance from Harvard Health Publishing which emphasizes the importance of nutrient synergy for collagen production.
Collagen Supplements Explained
Collagen supplements are typically derived from bovine, marine, or poultry sources and processed to improve digestibility, with absorption dynamics evaluated in clinical nutrition research analyzing peptide bioavailability and systemic utilization.
Hydrolyzed Collagen (Collagen Peptides)
Hydrolyzed collagen is broken down into smaller peptides for improved absorption, with metabolic studies published by the National Institutes of Health demonstrating how collagen peptides are absorbed and distributed throughout the body.
Multi-Collagen Formulas
Multi-collagen supplements combine multiple collagen types sourced from different animals to provide broader tissue support, a formulation strategy discussed in nutritional science research evaluating synergistic collagen intake.
How to Support Natural Collagen Production
Collagen production can be supported naturally by consuming vitamin C-rich foods, avoiding excessive sugar intake, protecting skin from UV exposure, prioritizing quality sleep, and engaging in regular strength training, with lifestyle guidance supported by clinical education from Cleveland Clinic emphasizing habits that reduce collagen breakdown.